Bug Bites
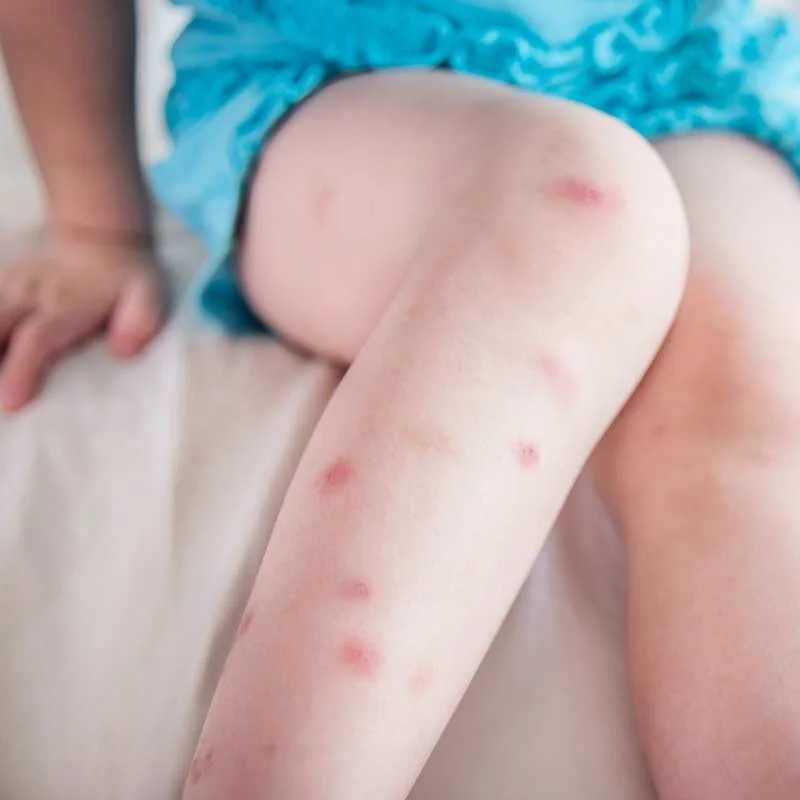
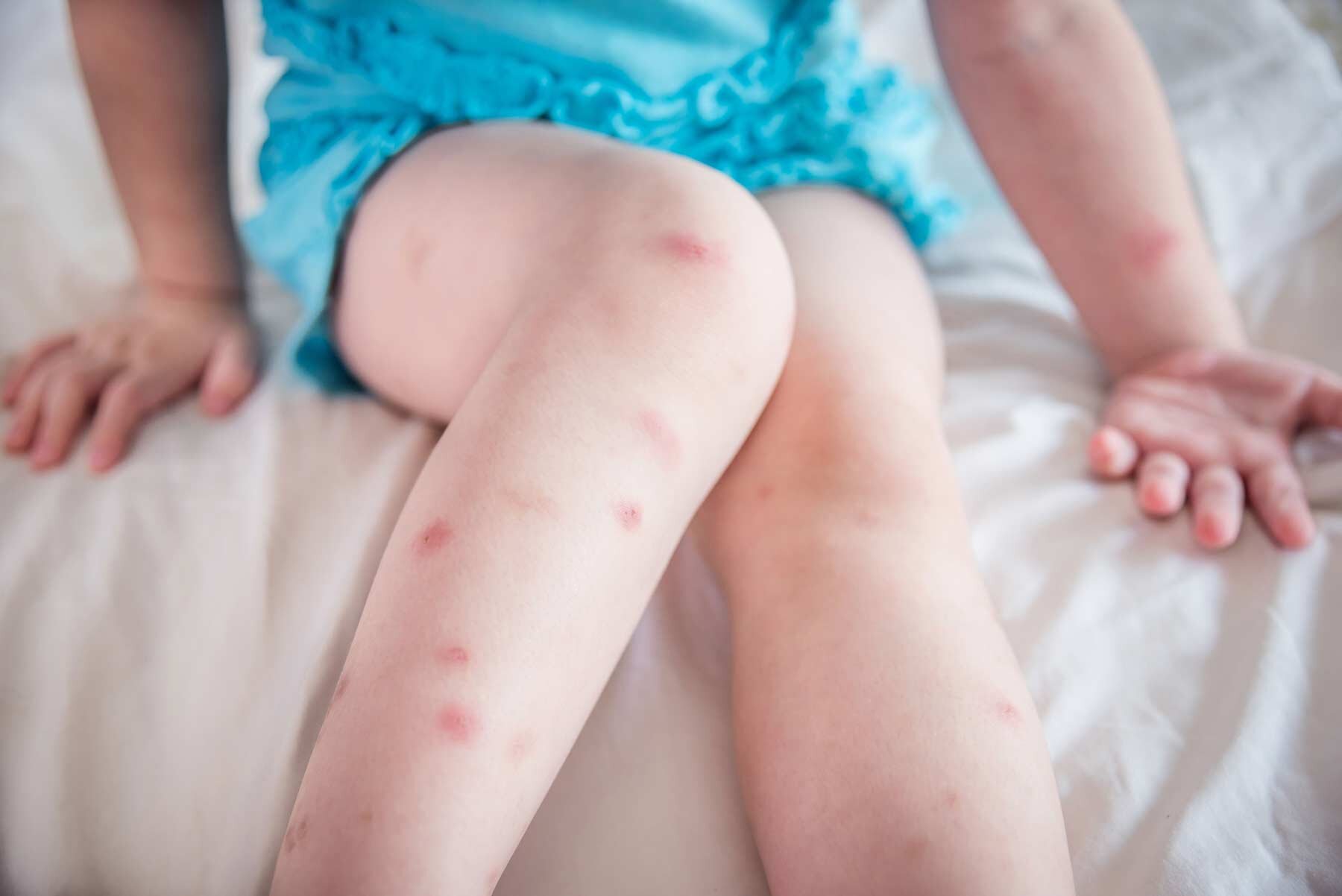
Bug bites are a common occurrence, especially during the warmer months when insects are most active. While most bug bites are harmless and cause only minor discomfort, some bug bites can transmit diseases and cause more serious health problems. Understanding the different types of bugs that bite and the symptoms and treatment of their bites can help to prevent and manage bug bite reactions.
One of the most common types of bugs that bite are mosquitoes. Mosquitoes are small, flying insects that are attracted to the carbon dioxide and heat that humans and animals give off. They bite to feed on blood, and their bites can cause red, itchy bumps on the skin. In some cases, mosquitoes can transmit diseases such as malaria, Zika virus, and West Nile virus through their bites.
Other common biting insects include:
Fleas: small, wingless insects that feed on the blood of animals and humans. Flea bites can cause red, itchy bumps on the skin, and can be especially problematic if they lead to a flea infestation in the home.
Bed bugs: small, reddish-brown insects that feed on the blood of humans and animals while they sleep. Bed bug bites can cause red, itchy bumps on the skin, and can be difficult to get rid of once they have infested a home.
Ticks: small, blood-sucking parasites that are commonly found in wooded or grassy areas. They attach to the skin and feed on blood, and their bites can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease.
Symptoms of bug bites can vary depending on the type of bug and the individual's reaction to the bite. Most bug bites cause red, itchy bumps on the skin, but some people may experience more severe reactions, such as hives, swelling, or difficulty breathing. In rare cases, bug bites can cause serious allergic reactions that may require emergency medical treatment.
Treatment for bug bites typically involves relieving symptoms and preventing infection. Over-the-counter creams and ointments, such as hydrocortisone cream, can help to reduce itching and inflammation. To prevent infection, it is important to keep the affected area clean and avoid scratching the bite. If the bite becomes infected or if you experience a severe allergic reaction, it is important to seek medical attention.
To prevent bug bites, there are several steps you can take:
Use insect repellents containing DEET or picaridin on exposed skin and clothing
Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when outdoors, especially in wooded or grassy areas
Use mosquito netting when sleeping outdoors or in unscreened areas
Check for ticks after spending time outdoors, and remove any ticks promptly
Keep your home and yard free of standing water, which can attract mosquitoes
By taking precautions and understanding the symptoms and treatment of bug bites, you can help to prevent and manage reactions to bug bites.