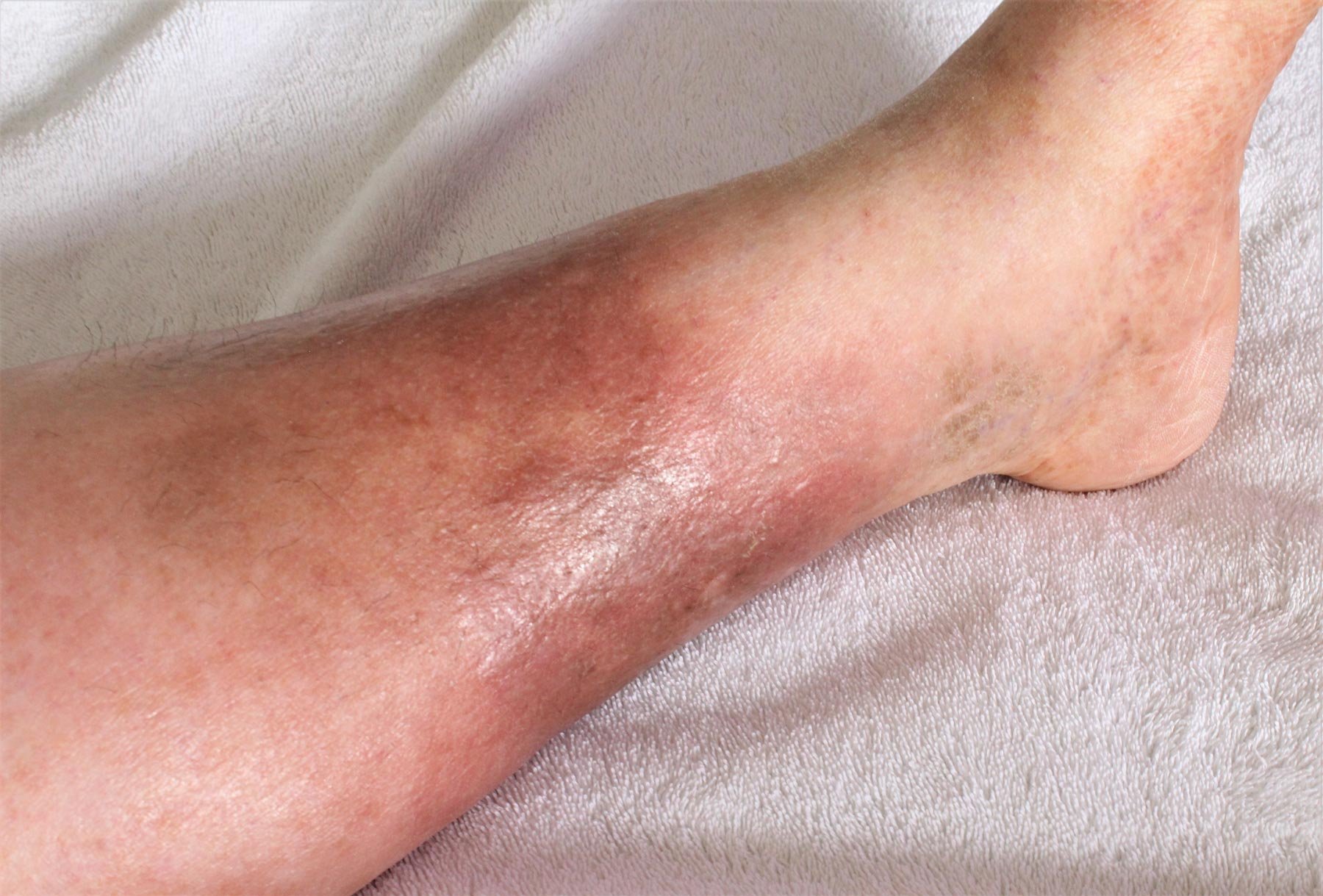
Cellulitis
Cellulitis is a serious bacterial infection that affects the skin and the underlying tissue. It is most commonly caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria, and can spread quickly if not treated promptly. Cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body, but is most common on the lower legs, arms, and face.
Symptoms of cellulitis include redness and swelling of the affected area, warmth to the touch, and pain or tenderness. The skin may also appear shiny or tight, and there may be red streaks leading away from the affected area. In severe cases, the affected area may feel hard or firm, and there may be fever, chills, and fatigue.
Cellulitis is usually treated with antibiotics, which can be administered orally or intravenously depending on the severity of the infection. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure proper treatment. It is important to complete the entire course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
To prevent cellulitis, it is important to keep the skin clean and moisturized, and to avoid cuts and scrapes. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV or AIDS, diabetes, or cancer, are at an increased risk for cellulitis and should take extra precautions to protect their skin.
It is also important to be aware of any changes in the skin, and to contact your dermatology provider if there are signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or warmth. Early treatment can help prevent the infection from spreading and becoming more severe.

