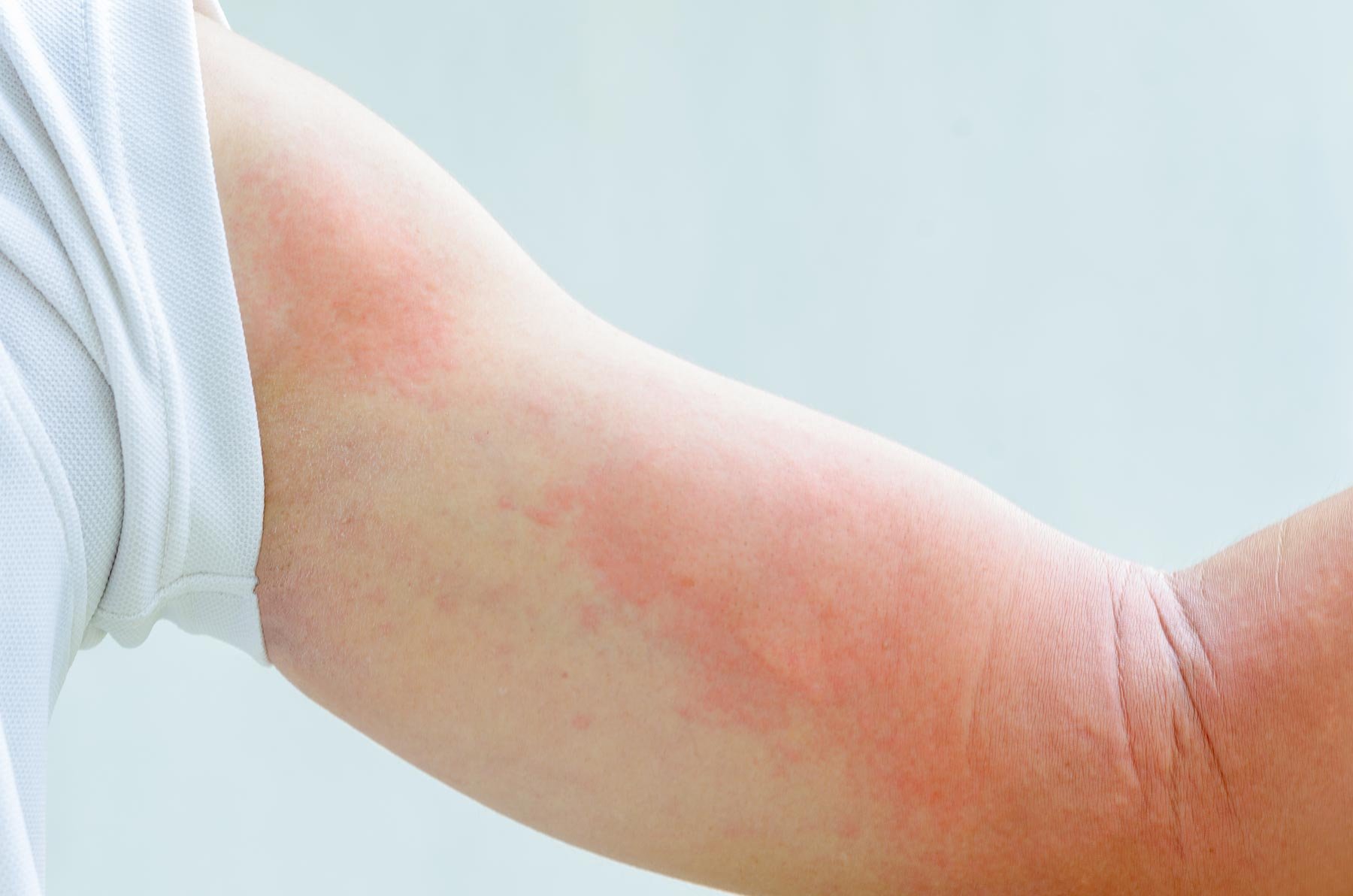
Drug Rashes
A drug rash, also known as a drug eruption or a drug-induced rash, is a skin reaction that occurs as a result of taking a medication. Drug rashes can range in severity from mild to severe and may involve a range of symptoms, including redness, itching, and hives. In some cases, a drug rash may also be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, joint pain, or swelling.
Drug rashes can be caused by a variety of medications, including prescription and over-the-counter drugs. They may occur within a few days or weeks of starting a new medication, or may not appear until several months after starting treatment. Some people may be more prone to developing drug rashes than others, but it is not always possible to predict who will experience this reaction.
There are several types of drug rashes, including:
Maculopapular rash: This type of rash is characterized by flat, red patches on the skin that may be accompanied by bumps. It is often caused by antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Urticaria: This type of rash is characterized by red, raised welts on the skin that may be itchy. It is often caused by antibiotics, blood pressure medications, and NSAIDs.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS): This is a severe, life-threatening reaction that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is characterized by the appearance of painful blisters on the skin and can be accompanied by fever and other symptoms. SJS is often caused by antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and NSAIDs.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN): This is a rare, severe reaction that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It is characterized by the detachment of the top layer of skin and can be accompanied by fever and other symptoms. TEN is often caused by antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and NSAIDs.
If you suspect that you have a drug rash, it is important to speak with a healthcare provider as soon as possible. They can help to determine the cause of your rash and recommend appropriate treatment. In some cases, the rash may resolve on its own once the offending medication is stopped. In more severe cases, treatment may involve the use of medications to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary.
If you are taking a new medication and develop a rash or other unusual symptoms, it is important to report these to your healthcare provider. They can help to determine the cause of your symptoms and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.

