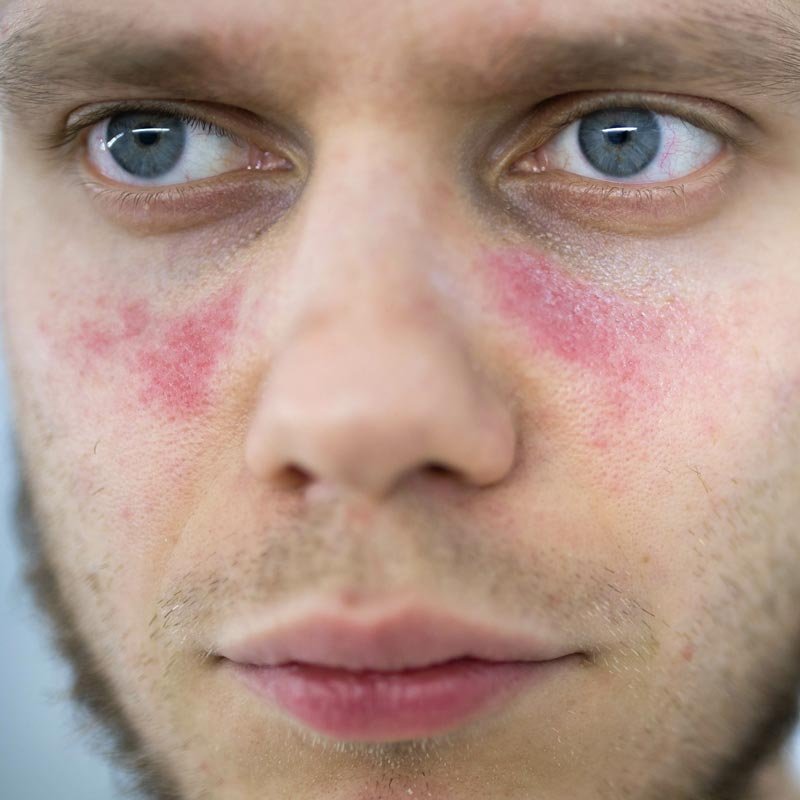
Lupus of the skin
Lupus is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack healthy cells and tissues in the body. Lupus can affect many different organ systems, including the skin, and may cause a wide range of symptoms.
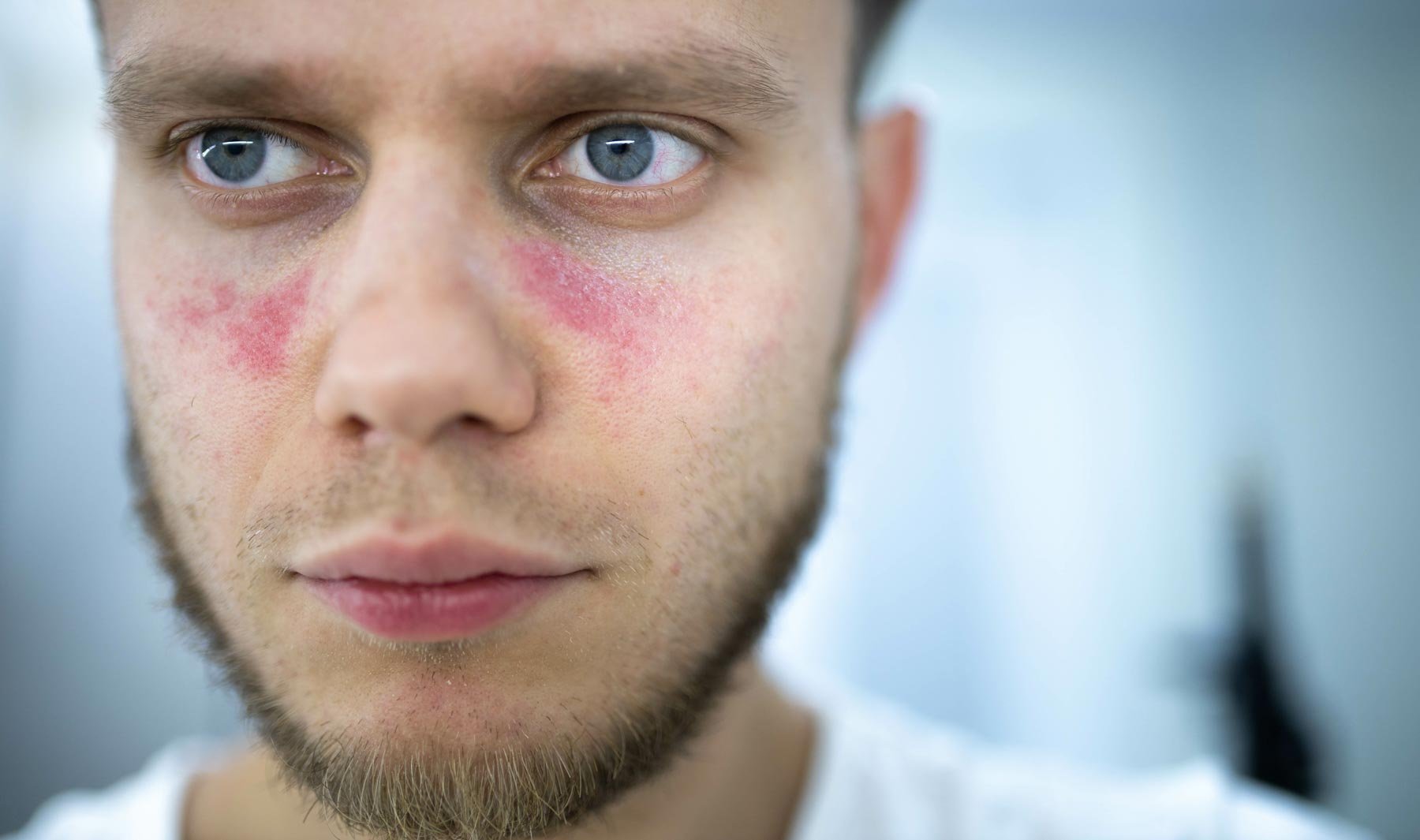
Lupus of the skin, also known as cutaneous lupus erythematosus, is a type of lupus that affects the skin and can cause a variety of skin lesions and rashes. The most common type of cutaneous lupus is discoid lupus erythematosus, which causes a rash on the face, neck, and scalp. Other types of cutaneous lupus include subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
Symptoms of lupus of the skin may include:
A rash or lesions on the skin that are red, raised, and scaly
Photosensitivity, or sensitivity to sunlight
Dry, itchy skin
Changes in skin color
Hair loss
Treatment for lupus of the skin may involve the use of topical medications, such as corticosteroids, to help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Systemic medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or immunosuppressants, may also be recommended to help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. In some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend phototherapy (exposure to controlled amounts of UV light) or other treatments, such as plasmapheresis (a procedure that removes antibodies from the blood) or rituximab (a monoclonal antibody).
In addition to treatment, there are several steps you can take to help manage lupus of the skin:
Protect your skin from the sun by wearing protective clothing, such as a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses, and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher
Avoid using harsh soaps or detergents that may irritate your skin
Use a mild moisturizer to help hydrate and protect your skin
Avoid scratching or picking at the affected areas, as this can cause infection or scarring
By following these precautions and seeking treatment as needed, you can help to manage lupus of the skin and reduce your risk of developing this type of autoimmune disorder. If you are concerned about lupus or have any other changes in your skin, it is important to see a healthcare provider for evaluation and treatment. Early detection and treatment can help to prevent the condition from worsening and may improve the chances of a successful outcome.