Melanoma
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the skin. It is the most serious type of skin cancer and can spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Melanoma can occur on any part of the body, but it is most commonly found on the face, chest, back, and legs.
Melanoma is caused by exposure to UV radiation, which damages the DNA in the skin cells and can lead to the development of cancerous cells. Risk factors for melanoma include:
Fair skin: people with fair skin are more likely to develop melanoma than those with darker skin
Sun exposure: prolonged exposure to UV radiation, particularly sunburns, can increase the risk of melanoma
Family history: people with a family history of melanoma are more likely to develop the disease
Moles: having more than 50 moles or moles that are large or irregularly shaped can increase the risk of melanoma
Symptoms of melanoma may include the development of a new mole or the changes in the appearance of an existing mole, such as an increase in size, irregular borders, or a change in color. Melanoma may also cause itching, bleeding, or a change in the texture of the affected area.
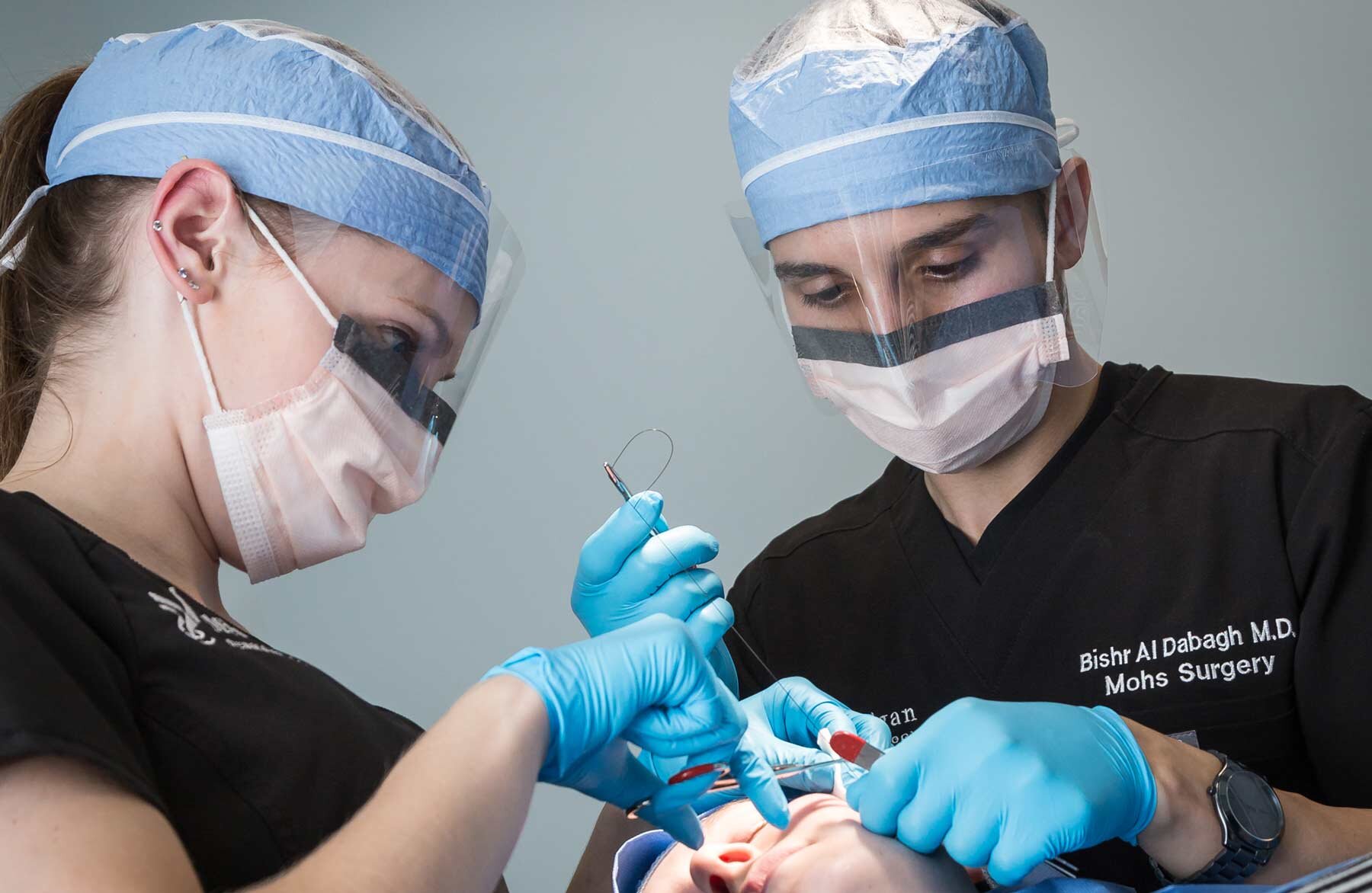
Treatment for melanoma typically involves surgical removal of the affected area, as well as any surrounding tissue that may be affected. In some cases, additional treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, may be recommended to help prevent the spread of the cancer. The specific treatment recommended will depend on the location, size, and stage of the melanoma.
In addition to treatment, there are several steps you can take to help reduce your risk of developing melanoma:
Avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the sun is strongest
Wear protective clothing, such as a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses, when you are outdoors
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on a daily basis, even on cloudy days
Avoid using tanning beds
Perform regular self-exams to check for any unusual or suspicious spots on your skin
By following these precautions and seeking treatment as needed, you can help to manage melanoma and reduce your risk of developing this type of skin cancer. If you are concerned about melanoma or have any other changes in your skin, it is important to see a healthcare provider for evaluation and treatment. Early detection is key to improving the chances of a successful outcome.

