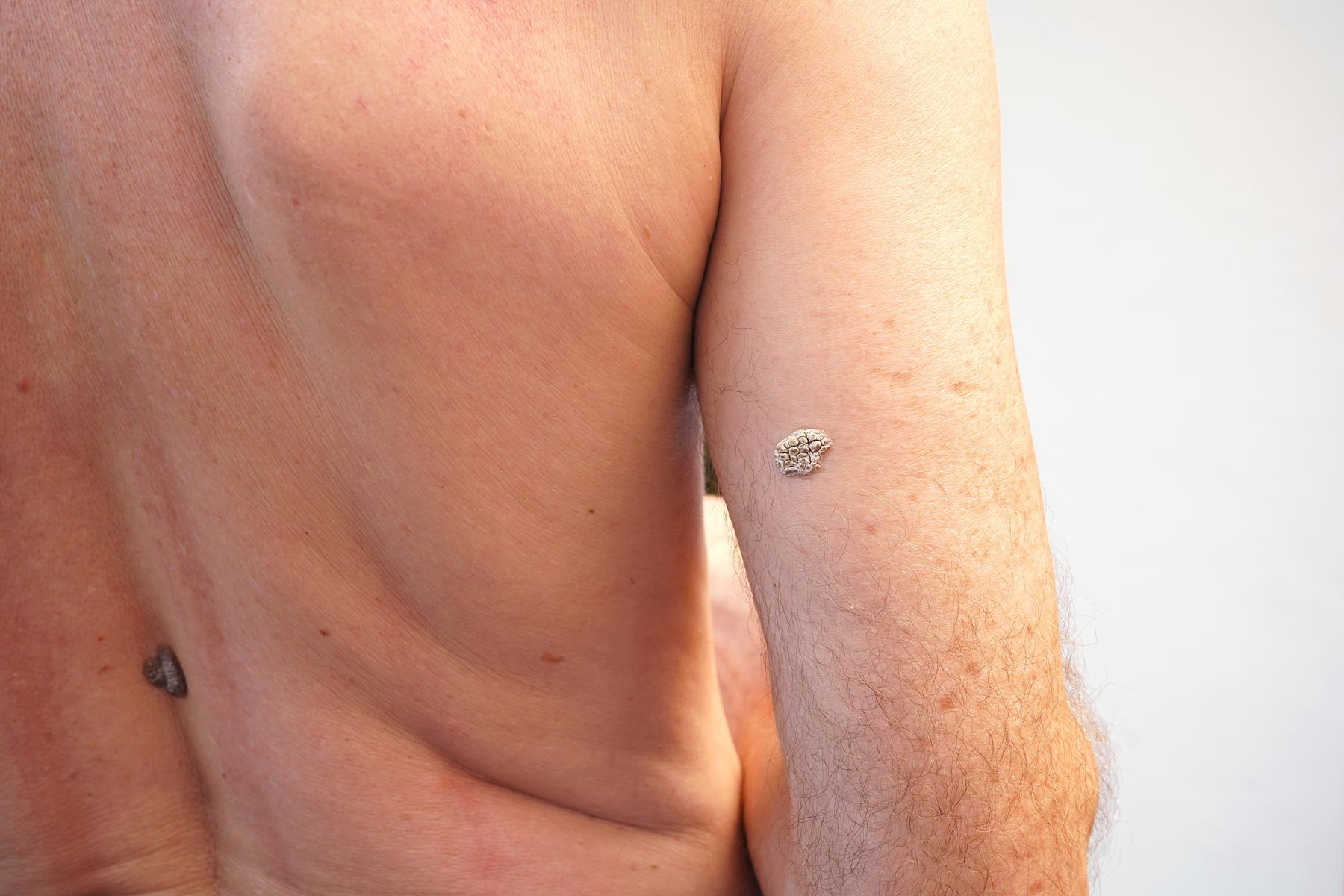
Seborrheic Keratosis
Seborrheic keratosis is a common skin condition that is characterized by the presence of raised, wart-like growths on the skin. It is a benign (non-cancerous) condition that can occur at any age, but it is more common in older adults. Seborrheic keratosis is not contagious and is not caused by poor hygiene.
The exact cause of seborrheic keratosis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to the natural aging process and sun exposure. Other factors that may contribute to the development of seborrheic keratosis include:
Family history: people with a family history of seborrheic keratosis are more likely to develop the condition
Sun exposure: prolonged exposure to UV radiation can increase the risk of seborrheic keratosis
Fair skin: people with fair skin are more likely to develop seborrheic keratosis than those with darker skin
Symptoms of seborrheic keratosis may include the presence of raised, wart-like growths on the skin that are brown, black, or tan in color. The growths may be smooth or rough in texture and may range in size from small to large. Seborrheic keratosis may be accompanied by itching or a burning sensation.
Treatment for seborrheic keratosis is generally not necessary, as the growths are benign and do not cause any symptoms. However, some people may choose to have seborrheic keratosis removed for cosmetic reasons or if the growths are causing irritation or discomfort. Treatment may involve the use of over-the-counter or prescription medications, such as creams or ointments, or surgical removal.
In addition to treatment, there are several steps you can take to help reduce your risk of developing seborrheic keratosis:
Avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. when the sun is strongest
Wear protective clothing, such as a wide-brimmed hat and sunglasses, when you are outdoors
Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher on a daily basis, even on cloudy days
Avoid using tanning beds
Perform regular self-exams to check for any unusual or suspicious spots on your skin
By following these precautions and seeking treatment as needed, you can help to manage seborrheic keratosis and reduce your risk of developing this type of skin condition. If you are concerned about seborrheic keratosis please see your dermatology provider.

